Docker Pull Command: How to Pull Docker Images

Docker has been a game changer in modern app deployment. It's the core component in the microservices architecture and DevOps. It eliminates dependency conflicts by isolating applications in containers, and in doing so, addresses the "it works on my PC only" puzzle.
In Docker, applications run in isolation inside containers, which are created from Docker images. Before we proceed, let’s see what a Docker image is.
#What is a Docker image?
A Docker image is a layered blueprint of a container. It's a read-only template that ships with all the components needed to run an application, including runtime environment, environment variables, application code, libraries, and dependencies.
#Prerequisites
To follow along with pulling Docker images, ensure you have the following:
- Docker is installed on your Linux instance. Our article demonstrates Docker installation on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS.
Ready to supercharge your Docker infrastructure? Scale effortlessly and enjoy flexible storage with Cherry Servers bare metal or virtual servers. Eliminate infrastructure headaches with free 24/7 technical support, pay-as-you-go pricing, and global availability.
#Searching and Pulling Docker Image
Let's now shift our focus to pulling Docker images. We will explore how to search and pull images from Docker Hub.
#How to search for a Docker image
Docker uses Docker Hub by default as the container registry of choice.
To look up an image from Docker Hub, employ the syntax:
docker search image_name
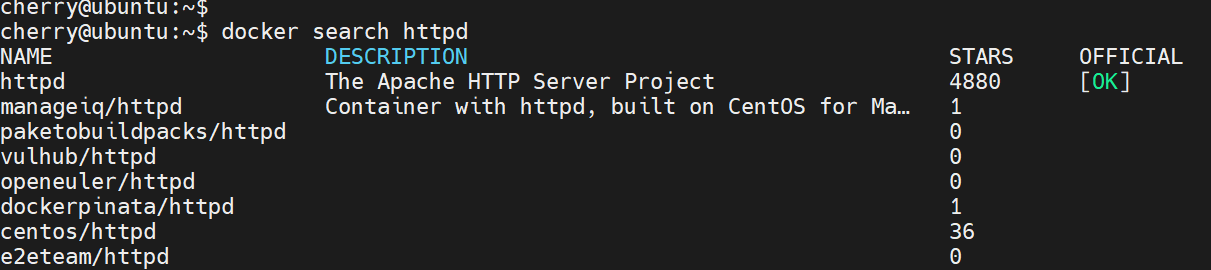
For example, to search for httpd, the Apache HTTP web server image, run:
docker search httpd
You get a similar output, showing all possible images that match the httpd string. The OK tag under the OFFICIAL column shows that the image is an official image and is currently maintained by the vendor.
#How to pull a Docker image
To pull or download a Docker image, run the docker pull command:
docker pull image_name
For example, to download the httpd image, run the command:
docker pull httpd
You get the following output.
OutputUsing default tag: latest
latest: Pulling from library/httpd
61320b01ae5e: Pull complete
be60498bea0a: Pull complete
4f4fb700ef54: Pull complete
8f86928406fd: Pull complete
162ef2c73af1: Pull complete
8dbbd44856ed: Pull complete
#Pulling a Docker image with a tag.
A Docker tag is simply a label assigned to an image to identify its variant or version. A tagged image takes the following format <image-name>:<tag>.
To pull an image with a tag, use the syntax:
docker pull image-name:tag
For example, to download Ubuntu 25.04, run the command:
docker pull ubuntu:25.04
Output25.04: Pulling from library/ubuntu
ceec33bc4ecc: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:10bb10bb062de665d4dc3e0ea36715270ead632cfcb74d08ca2273712a0dfb42
Status: Downloaded newer image for ubuntu:25.04
docker.io/library/ubuntu:25.04
Let’s take another example. To download the Redis image with a tag 8.0 run the command:
docker pull redis:8.0
Output8.0: Pulling from library/redis
61320b01ae5e: Already exists
2eadfe3f8ccb: Pull complete
7cd6cf8be223: Pull complete
b99b504f32ae: Pull complete
1db54fb7bf48: Pull complete
4f4fb700ef54: Pull complete
85952d2db39a: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:dbf3e4b6ad3ece9c733282ff3f16942ed754fdc4ea12332154f30a9a9b88c3af
Status: Downloaded newer image for redis:8.0
docker.io/library/redis:8.0
NOTE
When not specified, Docker defaults to using the latest tag when pulling an image. It does not imply that the image is the most current version. Rather, it is assigned to an image without a specific tag.
#Managing Docker images
Once you have downloaded your images, you might want to perform some housekeeping tasks, such as listing, inspecting, and removing images.
In this section, we will have a rundown of some of the management tasks you can perform with your images.
#Listing Docker images
There are two commands you can use to list Docker images on your local machine. You can run:
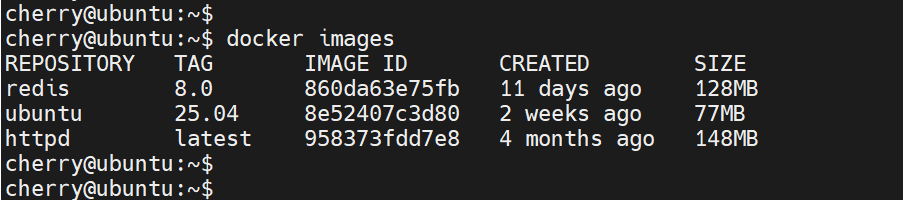
docker images
OR
docker image ls
Both commands yield the same output as shown.
The output is displayed in a tabular format. Let’s take a closer look and interpret the output.
REPOSITORY: This is the image name.
TAG: Represents the image version. The latest tag is applied by default if no tag is specified
IMAGE ID: A unique alphanumeric identifier for an image
CREATED: The date the image was spawned
SIZE: Image size on your local system's disk
#Inspecting Docker images
The docker inspect command displays the structure of your Docker image and helps you understand how the image is built. The command provides a comprehensive output in JSON format as shown.
docker inspect image_name
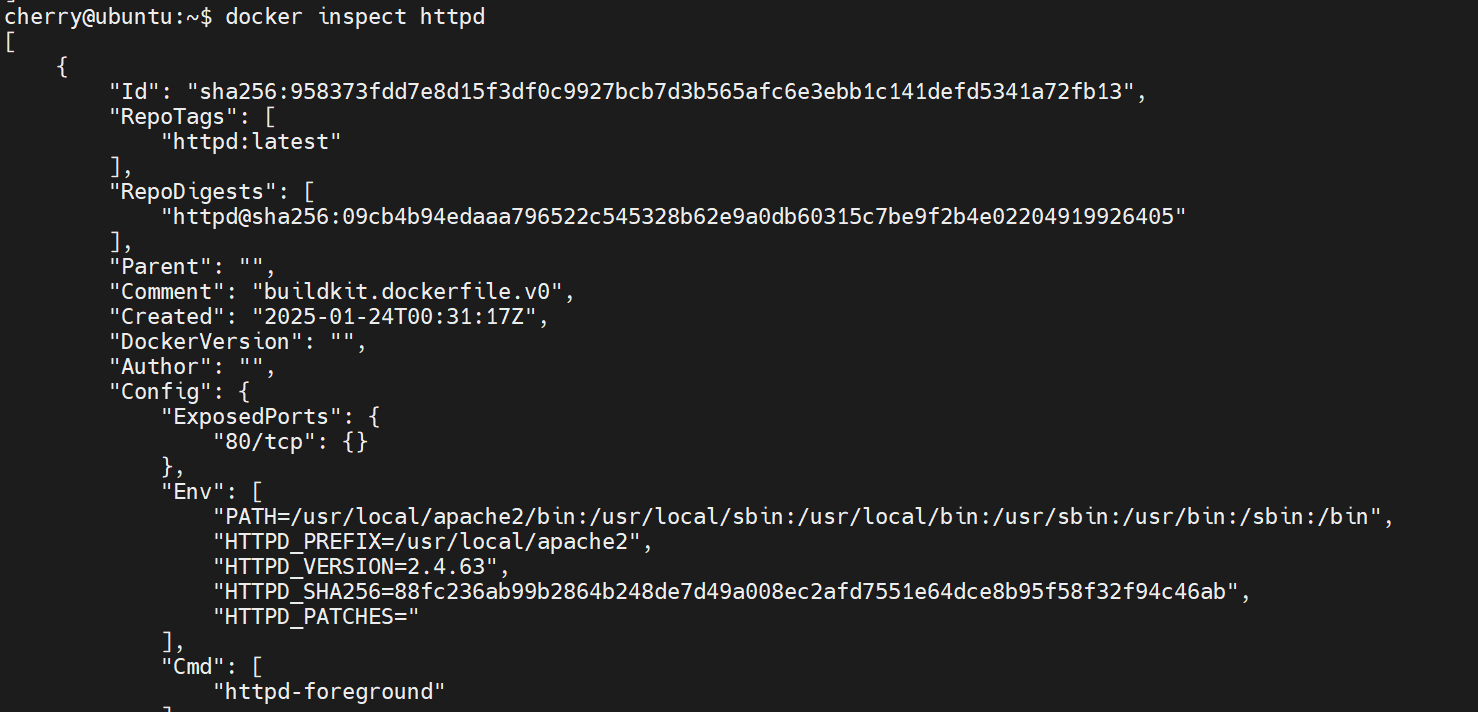
For example, to inspect the httpd image, run the command:
docker inspect httpd
The output includes salient image information, such as image metadata, configuration details, architecture, and file system structure.
For images associated with running containers, it displays the container(s) structure, mount volumes, and network information such as IP addresses, port bindings, security information, etc.
#Removing Docker images
If you have unused Docker images in your environment, it’s good practice to delete them to free up disk space on your system.
To remove or delete images, use the syntax:
docker rmi image_name
For example, to remove the redis:8.0 image, run the command:
docker rmi redis:8.0
The output below confirms the successful removal of the image.
OutputUntagged: redis:8.0
Untagged: redis@sha256:dbf3e4b6ad3ece9c733282ff3f16942ed754fdc4ea12332154f30a9a9b88c3af
Deleted: sha256:860da63e75fbff07bcbf9a94dadb4c7eb5016427b56b124d6becd5e9c95573c0
Deleted: sha256:22943bc4498bb65fd1c80c60769d2eef68f97245ceab2adddda14c0dcb5b4654
Deleted: sha256:d3deaf1b39fa77835766148767e97ddcc5fed0878eb7c5396645a0b2af4e24ab
Deleted: sha256:d78f46730646911fb9fb5747fb6f6b3197acb4dcbb64dabef788340ae9d32f3f
Deleted: sha256:fd4a4bba681b66cee96a0fa00d43d19f9704e3727ba63ff1daa49fddd902e4d2
Deleted: sha256:7448ebec06057f186bab15341cc295fddf7f80c510da780a1c472fb6ac4eb4c1
Deleted: sha256:cc5e954d8083a7a26b02f9bb25a2a8da118f8fd0261f5dea43a1ceb17a4b225e
NOTE
To remove an image associated with a container, you must first remove the container. If you still have a container that's still using the image or has exited, a warning will be displayed showing that Docker encountered an error.
In this example, we are removing a httpd Docker image associated with a running container whose ID is f711291aeb60.
First, we need to remove the container. To do this, run the following Docker commands:
docker stop f711291aeb60 && docker rm f711291aeb60
With the container removed, finally remove the Docker image:
docker rmi httpd
Alternatively, you can force remove an image using the -f option as shown:
docker rmi -f httpd
Use the docker images command to confirm successful removal of the image.
#Conclusion
This concludes the tutorial on pulling Docker images. Additionally, we took it a step further and demonstrated how to list, inspect, and remove Docker images. We hope you can comfortably pull and manage Docker images on your server.
Starting at just $3.24 / month, get virtual servers with top-tier performance.