What is Server Virtualization and How Does it Work?

Running one application on one server used to be the norm. Every new service meant new hardware, more space, and more maintenance. Server virtualization changed that. Now, one machine can run several virtual ones, each with its own system and apps, working as if it were a separate computer.
In this article, we will break down what server virtualization is, how it works, and where it is being used today.
#What is server virtualization?
Not too long ago, running more than a few applications meant stacking up physical servers—one for each task. It did the job, but not without headaches. Costs piled up, setups took time, and most servers sat there using just a fraction of their power. It was like owning a dozen cars but only driving each one once a week.
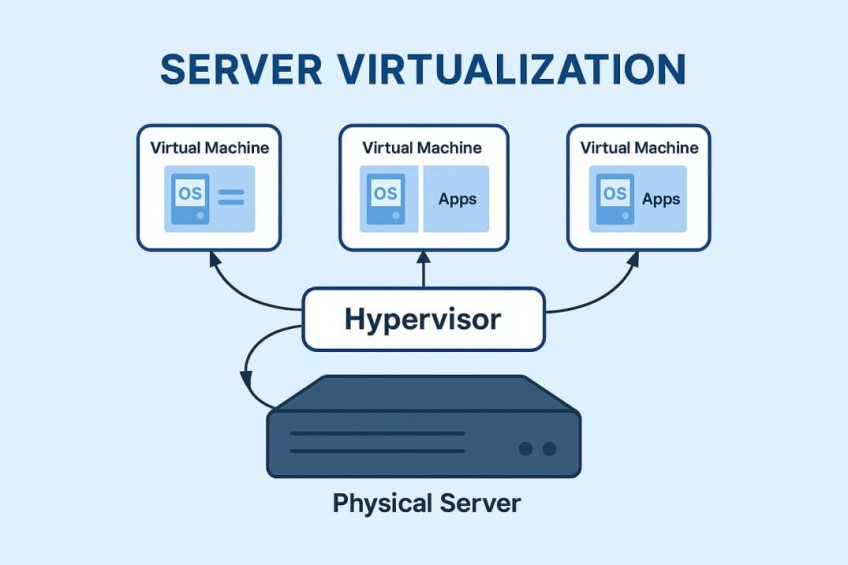
Server virtualization changed the game. Instead of setting up a new server every time you need to run something different, virtualization lets you break one machine into several virtual servers. Each one runs its own operating system and apps independently from the others. A hypervisor shares the server’s memory, storage, and processing power behind the scenes so everything runs smoothly.
With this setup, teams can run more apps, make better use of their hardware, and spend less time dealing with physical machines.