Virtualization vs. Containerization | Differences + Pros and Cons

Over the years, businesses have shifted infrastructure from physical servers to more efficient technologies like virtualization and containerization for faster application deployment and a streamlined software development lifecycle. These technologies have revolutionized application management by enabling scalability, rapid deployment, and cost optimization, to mention a few.
In this tutorial, we will compare the virtualization vs. containerization technologies, explore the key differences between the two, and highlight the pros and cons of each.
#Virtualization vs. containerization: key differences
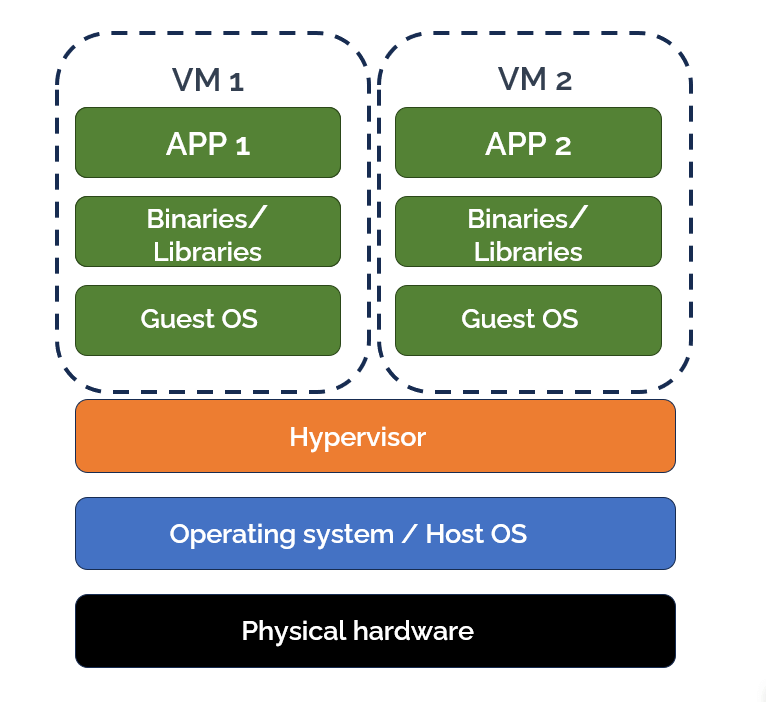
Virtualization allows you to create virtual machines (VMs) from underlying hardware resources using an abstraction layer known as a hypervisor. You can create and launch multiple virtual machines from a single physical machine, each running a different operating system. Virtual machines share the same resources, such as memory, storage, and processors, with the host system they are running on.
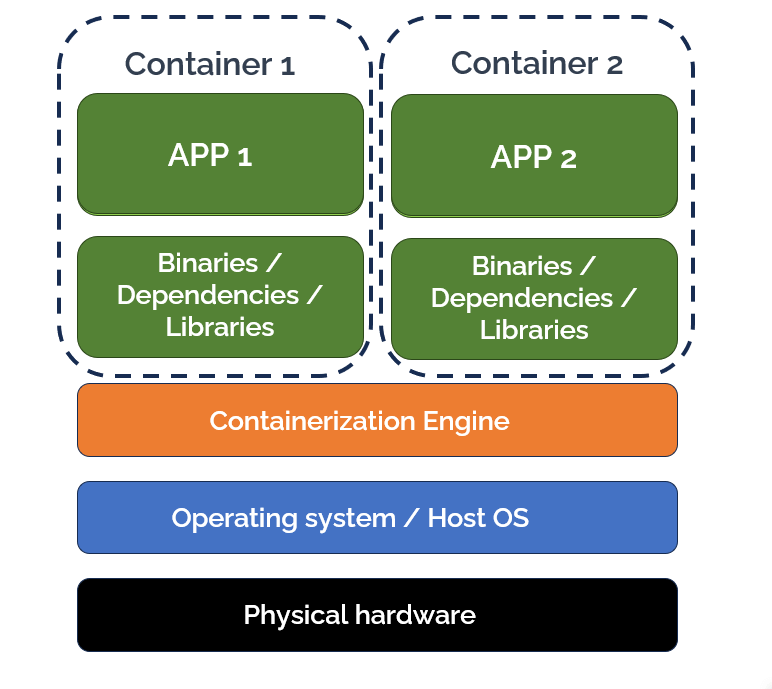
Containerization is a form of virtualization in which an application is bundled along with its code, libraries, dependencies, and everything else needed for it to run inside a component known as a container. A container is a lightweight and portable unit that runs consistently across any computing platform. Containers are more resource-efficient and scalable than virtual machines. Unlike VMs, they share the same OS kernel as the host, and there’s no abstraction of hardware resources. Containers are key components of microservices architecture and form an integral part of Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD).