How to Install .deb File in Ubuntu | Step-by-Step | 4 Methods

The software distribution landscape is constantly evolving. In Linux environments like Debian and Ubuntu, .deb files are essential packages for software deployment. This step-by-step guide will show how to install .deb file in Ubuntu 22.04. We will also discover what .deb files are and why they are necessary for managing software on your system.
#What is a .deb file?
A .deb file is a package format used in Debian and Debian-based Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu, Linux Mint, or Kali Linux. This software package contains everything needed for installation: the program’s files, details about the software, and scripts to manage the installation process.
#Prerequisites
To follow along this tutorial and install deb packages, you will need the following:
- A system account with administrative privileges;
- The latest Ubuntu version 22.04 installed.
Not using 22.04? Check out How to Install .deb Files on Ubuntu 24.04
#How to install .deb file in Ubuntu: 4 Methods
We will cover four different methods to install deb files in Ubuntu, from using the Graphical User Interface (GUI) to using the terminal. We install the browser Opera using the .deb file that you can download from their website.
Your browser will download the file by default in the Downloads folder.
#How to open a .deb file?
A .deb file being nothing more than an archived file, you can easily open and view its content with the following steps:
- Right-click on the
.debfile - Select
open With Archive Manager
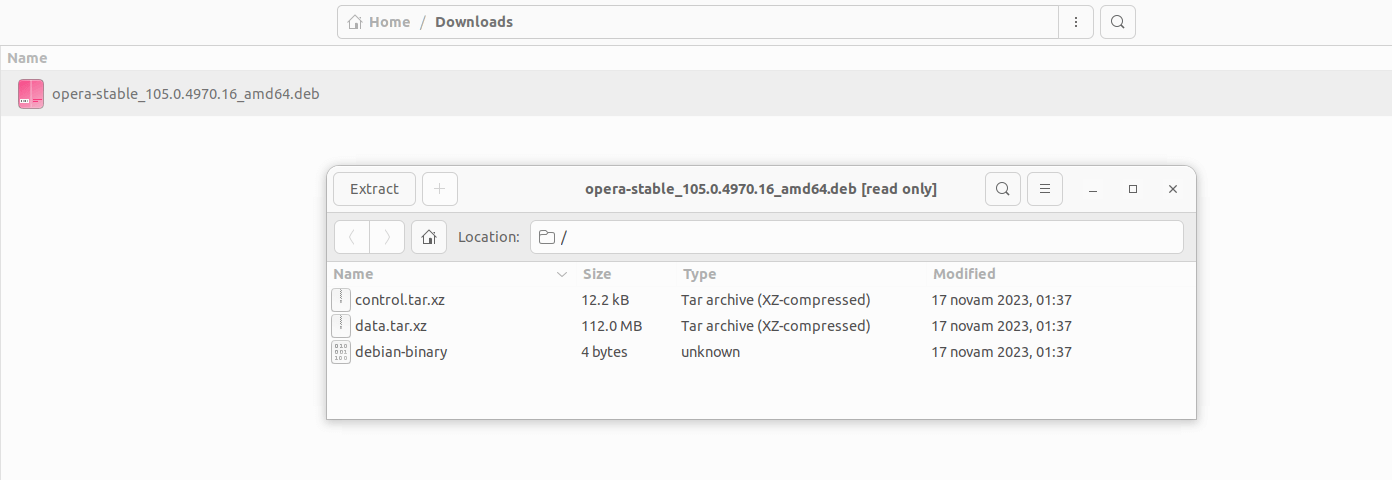
This will show you the content of the .deb file, as shown below:
We can see that the archive contains three files, namely:
- control archive: it contains the maintainer scripts and the package meta-data such as the package name, version, dependencies, etc.;
- data archive: it contains the actual files to install;
- debian-binary: it contains the package format version number.
We will now go through the different methods to install the .deb file.
#Method 1: Install .deb file using APT
The simplest way to install a .deb file is using the apt command, which is installed by default on Ubuntu.
Run the following command in the Downloads folder to install the .deb file:
sudo apt install ./opera-stable_105.0.4970.16_amd64.deb
#Method 2: Install .deb file using dpkg
The dpkg package provides the low-level infrastructure for handling Debian software packages. It is installed by default on Ubuntu.
We can now install the .deb file using the following command:
sudo dpkg -i opera-stable_105.0.4970.16_amd64.deb
#Method 3: Install .deb file using gdebi GUI
gdebi is a software that allows you to install local deb packages, resolving and installing the .deb dependencies. It also contains a graphical user interface.
#Step 1: Install gdebi
You can install gdebi using the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt install gdebi
#Setup 2: Launch gdebi-gtk
You can now launch the GUI part of gdebi by typing gdebi-gtk:
gedbi-gtk
#Step 3: Open the .deb file
We will now open the .deb file we downloaded before using gdebi-gtk:
- Click on
File - Click on
Open - Browser through your
Downloadsfolder - Select the
.debfile
#Step 4: Install the package and dependencies
Now that the .deb file is loaded, gdebi will display all the information related to it.
Click on the button Install package to continue.
Once the installation is complete, you can close the gdebi interface.
#Method 4: Install .deb file using gdebi command
As gdebi is already installed, we can run the following command to install the .deb file in the terminal:
sudo gdebi opera-stable_105.0.4970.16_amd64.deb
This will unpack and install the content:
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
Reading state information... Done
Fast, secure, easy-to-use web browser
Opera is a fast, secure, and user-friendly web browser.
It includes a built-in ad blocker, Video pop-out, and free VPN.
Do you want to install the software package? [y/N]:y
/usr/bin/gdebi:113: FutureWarning: Possible nested set at position 1
c = findall("[[(](\S+)/\S+[])]", msg)[0].lower()
Selecting previously unselected package opera-stable.
(Reading database ... 207576 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack opera-stable_105.0.4970.16_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking opera-stable (105.0.4970.16) ...
Setting up opera-stable (105.0.4970.16) ...
update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/opera to provide /usr/bin/x-www-browser (x-www-browser) in auto mode
update-alternatives: warning: skip creation of /usr/share/man/man1/x-www-browser.1.gz because associated file /usr/share/man/man1/opera.1.gz (of link group x-www-browser) doesn't exist
update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/opera to provide /usr/bin/gnome-www-browser (gnome-www-browser) in auto mode
update-alternatives: warning: skip creation of /usr/share/man/man1/gnome-www-browser.1.gz because associated file /usr/share/man/man1/opera.1.gz (of link group gnome-www-browser) doesn't exist
Processing triggers for mailcap (3.70+nmu1ubuntu1) ...
Processing triggers for gnome-menus (3.36.0-1ubuntu3) ...
Processing triggers for desktop-file-utils (0.26-1ubuntu3) ...
Processing triggers for hicolor-icon-theme (0.17-2) ...
Processing triggers for shared-mime-info (2.1-2) ...
Also read: Top 20 Linux Network Commands
#Conclusion
In this tutorial, we showed how to install .deb file in Ubuntu using four different methods, from terminal to GUI. Nowadays, most of the tools used for installation manage the dependencies, which makes the process easier. You can read more about the Debian package on the official Debian wiki.
Starting at just $3.24 / month, get virtual servers with top-tier performance.