Top Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms Explained

Blockchain depends on consensus mechanisms to maintain a decentralized and secure ledger. These protocols let network users agree on data status. Moreover, public blockchains do not require a central authority. It is important to understand consensus mechanisms if you work with distributed systems. They are essential for blockchain security and integrity.
This guide covers consensus mechanisms. It looks at different types and shows how they help nodes agree. By the end of this article, you will learn how consensus protocols build trust and fight fraud in blockchain networks.
#What are consensus mechanisms?
Consensus mechanisms are rules that help everyone in a blockchain agree on data. They make sure all nodes check transactions correctly. This teamwork secures the network. These protocols prevent fraud and protect against problems like double-spending and Sybil attacks.
Consensus mechanisms are key for trust in a trustless environment. They enforce rules that keep everyone honest. A strong consensus mechanism needs high security, scalability, efficiency, and fault tolerance. These features let the network process transactions quickly and accurately, keeping it reliable as it grows.
Think of a group vote where each person's input matters. In a blockchain, each node "votes" on the ledger's state. This ensures all votes lead to the same outcome. This analogy shows how consensus mechanisms keep the network synchronized and data secure.
Set up your Web3 server in minutes
Optimize cost and performance with custom or pre-built dedicated bare metal servers for blockchain workloads. High uptime, instant 24/7 support, pay in crypto.
#The role of consensus in blockchain
Consensus is important in blockchain technology. It ensures all nodes agree on one version of the ledger. This agreement builds trust and reliability in decentralized networks. Consensus protocols set the rules for nodes when they validate and record transactions. Each node "votes" on transaction validity. When most nodes agree, those transactions are added to the blockchain. In Bitcoin, consensus uses the Proof-of-Work method. Here, miners solve complex puzzles. When they succeed, they can add a new block.
These protocols prevent double-spending and block attempts to corrupt the network. Consensus mechanisms follow strict validation rules. This method removes the need for a central authority and reduces fraud risk.
Additionally, consensus mechanisms keep blockchain networks secure and functioning well. They ensure all participants agree on the network's state. They create a trustless system. Each node checks data on its own, yet the system works together as one. The balance between decentralization and coordinated validation makes blockchain secure and scalable.
#Types of consensus mechanisms
Below are the main consensus mechanisms used in blockchain systems.
#Proof-of-Work (PoW)
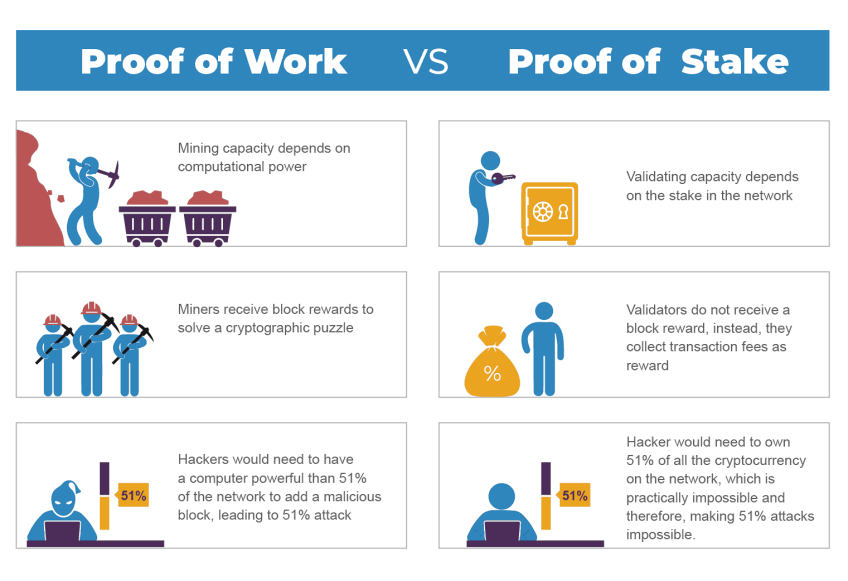
PoW requires miners to solve tough math puzzles. This process confirms transactions and adds new blocks. Miners compete to find a valid hash that fits the network's difficulty target. When a miner finds this hash, the network checks it and adds the block. Bitcoin uses the PoW mechanism.
PoW requires miners to use a lot of computing power. This method consumes considerable energy, sparking environmental concerns. The high energy costs can also lead to centralization among miners.
#Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
PoS picks validators based on the number of coins they hold and lock as collateral. Validators create new blocks in proportion to their stake, reducing energy consumption compared to PoW. Ethereum now uses PoS, as detailed in Ethereum docs. Validators may lose some of their stake if they validate fake transactions. This process is known as slashing. This incentive makes them honest and usually leads to quicker transactions. PoS boosts scalability and lowers environmental impact. However, it can cause wealth concentration.
#Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)
DPoS builds on the PoS model by introducing a voting mechanism. Token holders vote for a few delegates. These delegates validate transactions and create blocks. This system speeds up block production and reduces latency. It does this by having fewer nodes in the consensus process. However, concentrating power among a few delegates may create centralization risks.
#Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT)
PBFT helps nodes agree on transactions. This works even if some nodes act poorly or fail. It requires several rounds of messages to come to a consensus. This feature makes PBFT a good fit for permissioned blockchains. In these blockchains, participants have different levels of trust.
Hyperledger Fabric uses a PBFT variant. This helps it achieve quick finality and high transaction rates. PBFT can cope with up to one-third of nodes failing while still achieving agreement. However, its communication demands can slow down scalability in larger networks. For further details, see the Hyperledger Fabric Documentation.
#Other consensus mechanisms
Several alternative consensus protocols have emerged to address specific needs:
- Proof-of-Authority (PoA): PoA uses a small group of trusted validators to create blocks. It uses verified identities as stakes. This allows for quick transactions and saves energy. This method works well in trusted networks where everyone is known. However, it might lessen decentralization.
- Proof-of-History (PoH): PoH marks the time of transactions. This helps form a verifiable record of events before they join the consensus process. It uses a verifiable delay function to check the order of transactions. This helps cut down consensus time. This method boosts throughput and reduces latency. It is vital for networks like Solana.
- Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs): DAGs connect transactions as nodes. This setup lets transactions be processed in parallel, not just one after another. This design enhances scalability and can lower transaction fees significantly. These systems are great for apps that require high throughput and low fees, like IOTA's Tangle.
#Choosing the right consensus mechanism
Here are the main factors you should consider when picking a consensus mechanism.
#Security
Consensus algorithms secure the blockchain by preventing double-spending and attacks. Miners or validators must use a lot of computational power or stake. This way, only real transactions get confirmed.
For instance, PoW forces miners to solve complex puzzles, which deters attackers. This robust security layer builds trust across the network.
#Scalability and performance
Consensus mechanisms have a direct impact on transaction speeds and network latency. Algorithms like PoW can slow down transaction rates. They need a lot of computing power, which limits throughput. PoS and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance provide faster validation and better scalability. Choosing a scalable method lets you handle more transactions without slowing down.
#Decentralization and governance
Decentralization is important in blockchain technology. Consensus mechanisms divide power among network users. Protocols like PoW and PoS encourage broad participation. This prevents any one group from taking control of the ledger.
Some models, such as DPoS, assign validation power to a few chosen delegates. Finding the right balance between decentralization and efficiency impacts decision-making. This balance also shields the network from centralized control.
#Environmental impact
When choosing a consensus method, think about energy use. This matters a lot for energy-heavy methods like PoW. Mining operations using this method need a lot of power. They may have a large carbon footprint, depending on the energy source.
Recent studies show that moving to PoS can cut energy use by over 90%. This change helps the environment and cuts operating costs in the long run.
All these elements play a vital role in choosing the right consensus mechanism for your blockchain application. Examining security, scalability, decentralization, and environmental impact shows you the key technical trade-offs.
#Real-world use cases of consensus mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are crucial in many industries. They make sure that all transactions are verified and agreed upon. These mechanisms build trust in decentralized systems. They do this by preventing fraud and ensuring operations are secure and transparent.
Below are some real-world applications of consensus mechanisms.
#Cryptocurrencies
Consensus protocols protect digital currencies. They check each transaction and add it to the blockchain. Bitcoin works on a proof-of-work system. Miners solve complex puzzles to get rewards. Ethereum started with proof-of-work but now uses proof-of-stake. This change helps scalability and cuts energy use. These methods stop double-spending and fraud while keeping the ledger safe.
#Supply chain management
Blockchain boosts supply chain transparency. It tracks goods from production to delivery. Consensus methods confirm all transactions on the ledger, assuring data correctness and trustworthiness. IBM Blockchain uses these protocols to trace product origins and verify transactions. This approach reduces the risk of counterfeiting and streamlines complex supply chains.
#Financial services
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) apps use consensus mechanisms. These help secure and automate financial transactions. Ethereum and other platforms use smart contracts. These contracts run automatically when consensus is reached. This process cuts down the need for intermediaries. These protocols make financial services quicker and clearer. They also protect against fraud and hacking. The strength of these mechanisms is crucial to maintaining trust in financial networks.
#Enterprise applications
Private blockchains in businesses use consensus to keep sensitive data safe. Platforms like Hyperledger Fabric use consensus mechanisms. These mechanisms help achieve quick transaction finality and ensure fault tolerance. This is crucial for compliance in regulated industries.
#Internet of Things (IoT)
Consensus mechanisms support IoT networks by securing data exchange among countless connected devices. IOTA is an example of a project that uses distributed ledger technology for IoT. This keeps sensor data secure and verifiable. These systems handle many micro-transactions and data streams. They deliver reliable performance, even in complex settings. Consensus algorithms allow for decentralized decision-making. They help ensure data integrity across all devices in the network.
Each use case shows how important consensus mechanisms are in today's blockchain applications. They provide strong security, scalability, and trust. These are important for many industries that depend on decentralized technologies.
#Future trends in consensus mechanisms
Future trends in consensus mechanisms are evolving. Researchers are exploring hybrid models. These models blend strengths from different protocols. The aim is to boost scalability and cut energy use. Some hybrids combine the reliability of Proof-of-Work with the speed of Proof-of-Stake. This creates systems that lower computational demands while ensuring strong security. Researchers are also studying models that mix Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance with other methods. This enhances transaction finality and network resilience.
Advancements in quantum computing and distributed systems are set to transform consensus protocols. Quantum computing can speed up cryptographic operations. This may challenge current security standards and push for quantum-resistant algorithms.
#Conclusion
Consensus mechanisms are necessary for maintaining the security and trustworthiness of blockchain networks. They allow for agreement without a central authority. Moreover, they check transactions and block fraud. This is shown in systems like Bitcoin and Ethereum. These protocols build trustless environments. They need a lot of work or stake to validate data.
To wrap up, choosing the right consensus mechanism is crucial. It can really affect how blockchain applications perform, scale, and stay secure. Whether you go with proof-of-work, proof-of-stake, or another method, each has its trade-offs. These trade-offs can shape how they are used in real-life scenarios.