How to Install Postman on Ubuntu 24.04 | Step-by-Step

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on installing Postman on Ubuntu 22.04! Whether you're already familiar with Postman or completely new to it, this article is for you.
It will cover all the technical details related to installing the Postman application on Ubuntu 22.04 operating system. We will also discuss what Postman is, its importance, various use cases, and the different methods of how to install Postman on Ubuntu.
#Prerequisites
- A computer with Ubuntu 24.04 installed and running.
- A user account on your computer with privileges to install applications.
- A stable internet connection to download and test the Postman application.
#What is Postman?
Postman is a popular choice among API developers, API testers, and API consumers. You can use Postman for API development, testing, and documentation purposes, as it offers a simple and user-friendly interface for working with APIs.
Postman is available for all the main operating systems, such as Windows, Linux, and MacOS. Moreover, there is a web version if you want to avoid installing it on your computer. You can use the free version of Postman for most of your tasks. Furthermore, there is a Pro version that offers advanced testing features and team collaboration capabilities.
#What is Postman used for?
Postman offers a straightforward interface for developers to design, build, and modify APIs. Below are five use cases for Postman:
1. API testing: This is the most fundamental Postman use case. Developers and testers use Postman to manually send various HTTP requests (GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE) to API endpoints. They can easily configure request headers, body payloads in JSON or form-data, and query parameters. This allows them to inspect the responses, such as status codes and headers to verify if the API behaves as expected under different conditions.
2. Automated API testing: Postman allows users to write test scripts using JavaScript within their requests. These scripts can assert conditions on the response, such as:
- Checking the status code
- Validating JSON schema
- Verifying specific values in the response body
Collections of requests with tests can be run automatically using the Collection Runner or integrated into CI/CD pipelines.
3. API development & debugging: During the development phase, backend developers use Postman to test their API endpoints iteratively as they build them. Postman provides a quick way to send requests to local or development servers, inspect detailed responses, and check error messages. Features like environment variables allow easy switching between different development stages, such as local, dev, and staging.
4. API documentation generation: Postman Collections can be enriched with descriptions, examples of requests and responses, and detailed explanations for each endpoint. Postman can then automatically generate interactive, web-based API documentation from these collections. This documentation can be shared with frontend developers, making it easier for them to understand and integrate with the API.
5. API monitoring: Postman allows users to set up monitors that automatically run specific API test collections at scheduled intervals against deployed environments. This helps teams proactively check the health, performance, and correctness of their APIs in real-time. If any tests within the monitored collection fail, Postman can trigger alerts through email or Slack. This enables rapid response to production issues.
Postman can also be integrated with popular development tools like Git, Newman, and Jenkins. Other than that, Postman supports many other extensions and integrations to enhance its customization capabilities and functionalities.
#How to install Postman on Ubuntu 22.04: two methods
There are several methods to install Postman on Ubuntu. Below, we will go through each of the two ways. You can select the way that best suits your needs and follow the appropriate steps.
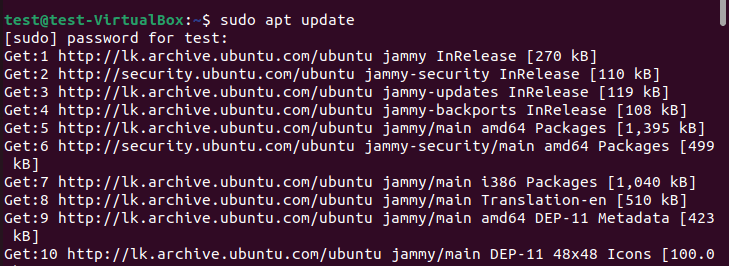
Whatever your chosen method, first, you need to update packages with the sudo apt update command. When you install a new application, it may have some dependency requirements. Updating your system will provide it with the latest requirements, which will help new applications work properly.
#Method 1: Install Postman using Snap
Snap is a package manager developed by the parent company of Ubuntu. It allows users to install, update, and manage software packages. You don’t have to install Snap, as it’s pre-installed on Ubuntu.
Run the following command to install Postman with Snap.
sudo snap install postman
You should first run the sudo apt install snapd command if somehow your operating system does not have the Snap package manager.
#Method 2: Install Postman using Flathub
Flathub is a software repository for Flatpak applications. Like the Snap package manager, Flatpak lets developers package applications and dependencies into bundles. To install Postman, you need to run the following command.
sudo apt install flatpak
Then you should add the Flathub repository (Flathub) by entering the below command.
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
Next, install Postman using the below command.
flatpak install flathub com.getpostman.Postman
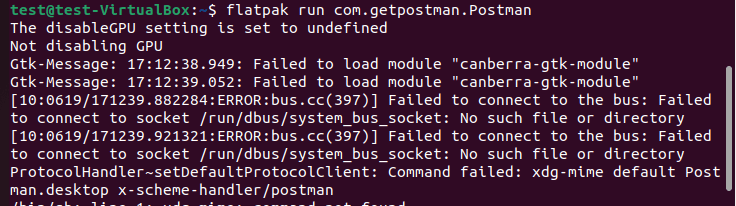
Once the installation is complete, you can start Postman by executing the flatpak run com.getpostman.Postman command.
Otherwise, you can always find Postman by searching for it on the Ubuntu application launcher.
#General Postman working environment guidelines for beginners
Launch Postman and explore different sections like the request builder, response viewer, and sidebar by yourself.
Create a simple GET request to a public API by entering the URL in the request builder, selecting the GET method, and clicking the “Send” button to send a request.
See the response in the response viewer as shown below.
Following the same steps, you can try other HTTP methods such as PUT, POST, and DELETE.
Other features include
- Creating collections and folders inside collections to categorize your requests in different ways.
- Setting query parameters and URL-encoded parameters.
- Creating simple tests and automating the API response validation process.
- You can experiment by generating documentation for your requests and trying to customize them.
- Sharing your collections or importing collections shared by others.
#How to uninstall Postman from Ubuntu: two methods
Now we will see how to uninstall Postman from our Ubuntu operating system. We will discuss the uninstallation process using the same two methods we discussed earlier.
#Method 1: Snap uninstallation
If you used the Snap package manager for installing Postman, you can uninstall Postman using the below command.
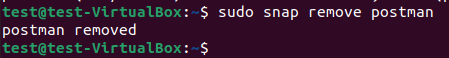
sudo snap remove postman
#Method 2: Flathub uninstallation
If you used the Flathub package manager for installing Postman, you can use the below command to uninstall Postman.
flatpak uninstall flathub com.getpostman.Postman
#Conclusion
Congratulations! Now you know how to install Postman on the Ubuntu operating system. Most importantly, you learned how to install and uninstall Postman using three different package managers. There is no special reason to use any one of them. The only thing to consider is the latest version available in each package manager. As long as the version available works for you, feel free to use the most familiar tool to install Postman.
Starting at just $3.24 / month, get virtual servers with top-tier performance.