How to Install PIP on Ubuntu 22.04 | Step-by-Step

In this step-by-step guide, we will walk you through how to install pip on Ubuntu 22.04. In addition, you will also learn how to install and uninstall Python packages using pip, as well as how to upgrade it to the latest version.
#What is PIP?
PIP, a recursive acronym for Pip Install Packages, is the standard package manager for Python. It uses the Python Package Index (PyPI) as the default software repository for installing Python packages.
PIP automates the installation of Python packages while handling dependencies. This eliminates the need for manual installation and ensures all dependencies required by the package are met. In addition, you can perform other operations such as listing, upgrading, and removing packages.
Deploy and scale your Python projects effortlessly on Cherry Servers' robust and cost-effective dedicated or virtual servers. Benefit from an open cloud ecosystem with seamless API & integrations and a Python library.
#Prerequisites
Before you roll your sleeves, ensure that you have the following requirements in place
- A running instance of Ubuntu 22.04 server.
- SSH access to the server with a sudo user configured.
Not using Ubuntu 22.04? Check our guide on How to install pip on Ubuntu 24.04
#Step 1: Confirm if Python is Installed
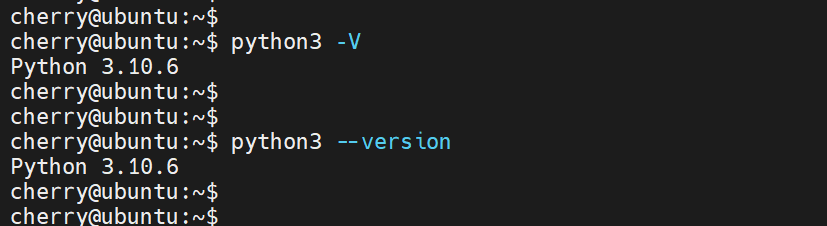
The first step is to ensure that Python is installed on your system. Thankfully, Ubuntu 22.04 provides Python 3.10 out of the box. You can confirm this by running the following command:
python3 -V
OR
python3 --version
The output below confirms that we have Python already installed.
If Python is missing from your system, install it using the following commands.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3 -y
#Step 2: Install PIP on Ubuntu 22.04
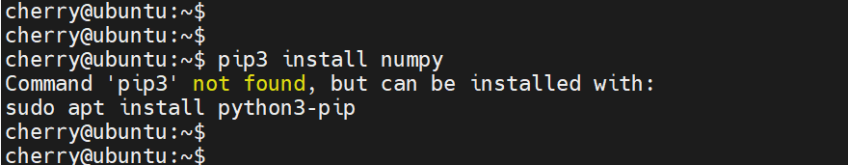
By default, pip is not installed. In fact, you run into an error when you try to install a Python package as shown here below.
pip3 install numpy
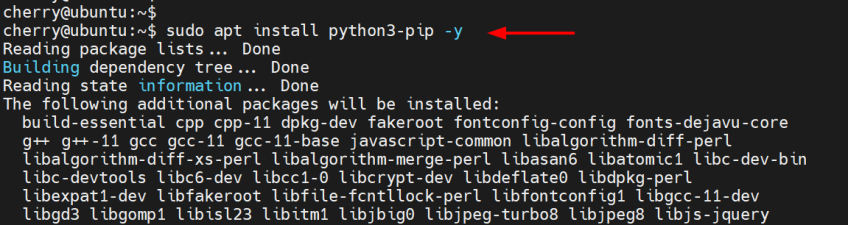
To install the latest version of pip, run the following command:
sudo apt install python3-pip -y
This installs pip3 alongside other additional packages, libraries, and dependencies.
Also read: How to install MongoDB on Ubuntu 24.04
#Step 3: Verify the Installation of PIP
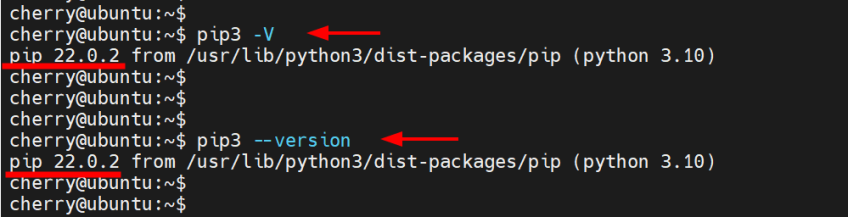
Once the installation is complete, verify that PIP is installed using the following command.
pip3 -V
OR
pip3 --version
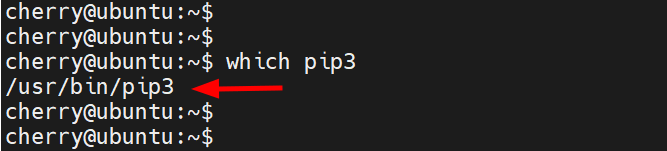
Additionally, you can verify the path of the executable file associated with the pip utility.
which pip3
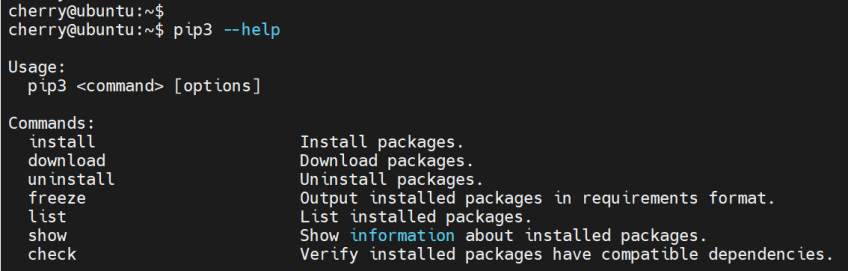
To get started with pip, you can list all the available options that are available using the package manager as shown.
pip3 --help
The output displays all the command-line options that can be used using pip.
You can narrow it down to a specific command option. For example, run the following command to display options associated with pip3 install.
pip3 install --help
Also read: How to install go file on Ubuntu 22.04
#How to Install and Manage Packages Using PIP
So far, we have successfully managed to install pip. To add the icing to the cake, we will go a step further and demonstrate how to use the pip package manager to install and manage installed packages.
To install a package, use the following syntax:
pip3 install package_name
For example, to install pandas, an open source Python library widely used in Data Science and Machine Learning, run the command:
pip3 install pandas
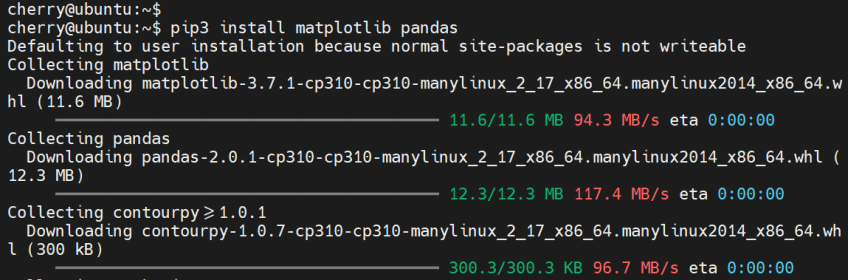
Additionally, you can install multiple packages in a single command. The following command installs pandas and matplotlib Python libraries.
pip3 install matplotlib pandas
To list installed Python packages, run the command:
pip3 list
The command lists all the installed Python packages. However, if you want to check if a specific package is installed, pipe the output to the grep command.
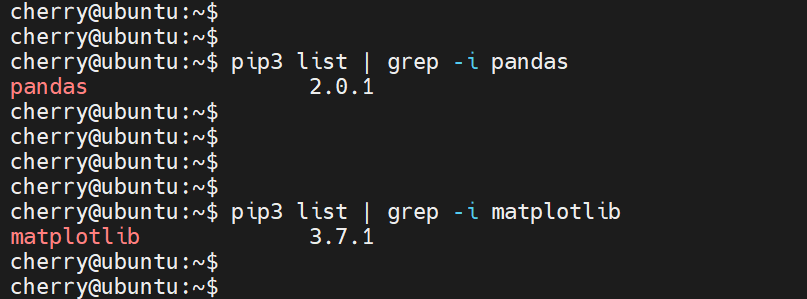
Here, we are checking for the existence of pandas and matplotlib Python packages on our system.
pip3 list | grep -i pandas
pip3 list | grep -i matplotlib
To display information about a specific package, use the syntax:
pip3 show package_name
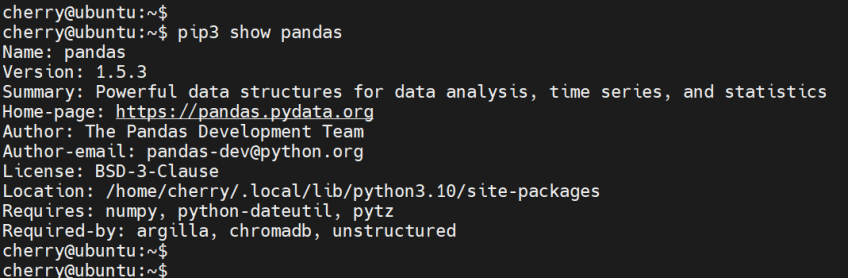
For example, to probe for information about the pandas package, run:
pip3 show pandas
The output provides information such as the name, version, author, and a brief summary of the package among other details.
To upgrade a Python package to its latest version, invoke the --upgrade or -U option.
pip3 install --upgrade package-name
pip3 install -U package-name
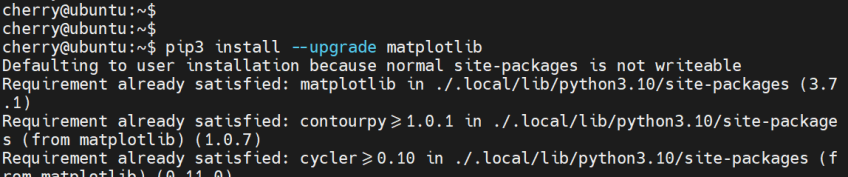
For example, to update the matplotlib package, run the command:
pip3 install --upgrade matplotlib
If the package is already in its latest version, no change will be affected.
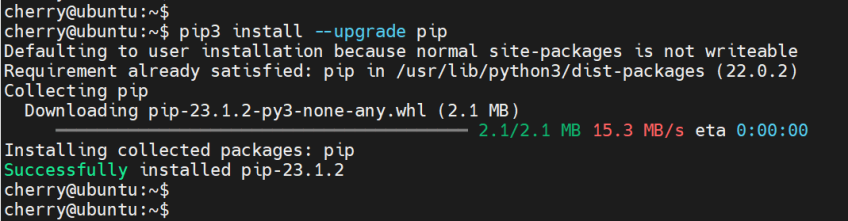
To upgrade pip itself to its latest version, run the command:
pip3 install --upgrade pip
To remove or uninstall a package, use the syntax.
pip3 uninstall package-name
For example, to remove Pandas, run the command:
pip3 uninstall pandas
Also read: How to install Wine on Ubuntu 24.04
#Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have demonstrated how to install pip on Ubuntu 22.04. In addition, we have gone the extra mile to show you how to use pip to install and manage already installed Python packages.
Starting at just $3.24 / month, get virtual servers with top-tier performance.