How to Connect to a Linux Server Using SSH
Secure Shell (SSH) is a widely used protocol for secure passwordless connection to a remote Linux server from any operating system, including Windows, Linux, or macOS. This guide walks you through the steps for connecting via SSH from different platforms.
Before you begin, ensure that you have your credentials, such as username and password, and the necessary privileges to access the server, and check if your server uses a non-standard SSH port. You will need to specify this with the -p option in your SSH command.
#Instructions to Connect to Your Linux Server with SSH
#Instructions to Connect to Your Linux Server with SSH from Linux or macOS
-
Open the Terminal:
- For Linux: Press Ctrl + Alt + T, or search for "Terminal" in your applications menu.
- For macOS: Open Spotlight using Command + Space, type "Terminal" and press Enter.
-
Enter the SSH command.
In the terminal, use the following command to initiate an SSH connection, replacing "username" with the username you want to log in with, typically root, and replace "IP_address" with the actual IP address or host name of your Linux server:
ssh username@ip_addressExample:
ssh root@5.199.162.89Returns:
Output
12:17:30 user@CherryServers ~ ssh root@5.199.162.89 The authenticity of host '5.199.162.89 (5.199.162.89)' can't be established. ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:A8DixBg9qB+xQFhpusH7KpLE/UNLZMn12N2JAkQyfQ. This key is not known by any other names Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes Warning: Permanently added '5.199.162.89' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts. -
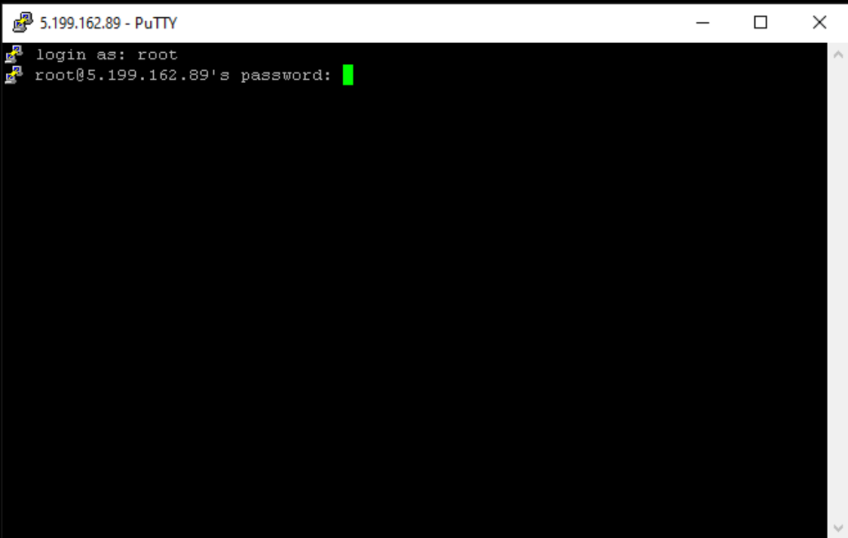
Provide your password.
After running the SSH command, you will be asked to enter your password. Type the password carefully and press Enter. Please note that for security reasons the password won't appear on the screen while typing for security reasons, but your input is still being recorded.
Output
root@5.199.162.89's password: -
Specify a custom SSH port, if applicable.
If your server is using a port other than the default SSH port (22), include the -p flag followed by the correct port number:
ssh username@ip_address -p custom_portReplace custom_port with the port number your server's SSH service uses. Example:
ssh user@5.199.162.89 -p 2222 -
Access the Server.
After successful authentication, you will be connected to the remote server, and you can start executing commands.
Output
Welcome to Ubuntu 22.04.5 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.15.0-119-generic x86_64) Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com Management: https://landscape.canonical.com Support: https://ubuntu.com/pro System information as of Mon Oct 7 12:51:26 EEST 2024 System load: 0.0 Processes: 87 Usage of /: 7.4% of 19.20GB Users logged in: 0 Memory usage: 19% IPv4 address for eth0: 5.199.162.89 Swap usage: 0% Expanded Security Maintenance for Applications is not enabled. 0 updates can be applied immediately. Enable ESM Apps to receive additional future security updates. See https://ubuntu.com/esm or run: sudo pro status The list of available updates is more than a week old. To check for new updates run: sudo apt update The programs included with the Ubuntu system are free software; the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright. Ubuntu comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by applicable law.
#Instructions to Connect to a Linux Server from Windows
On Windows, SSH connections can be made using either the built-in Windows terminal (available on Windows 10 and later), or third-party applications such as PuTTY.
#Option A: Using Windows Terminal (or PowerShell)
-
Open Windows Terminal or PowerShell.
- Press Windows + X, and select "Windows Terminal" or "PowerShell" from the menu.
- Alternatively, search for Windows Terminal or PowerShell in the Start menu.
-
Enter the SSH command.
In the terminal, run the following command, replacing "IP_address" with the IP address or host:
ssh username@ip_addressExample:
ssh root@5.199.162.89Output
C:\Users\Cherry>ssh root@5.199.162.89 The authenticity of host '5.199.162.89 (5.199.162.89)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:Gj7l1wurcTXy+dmUwkNANSq9mA+vInWmCBDVlxrh0M. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes Warning: Permanently added '5.199.162.89' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. -
Provide your password.
After entering the SSH command, you will be prompted to type your password. Enter it and press Enter. Once authenticated, you will be logged into the Linux server.
Output
root@5.199.162.89's password: -
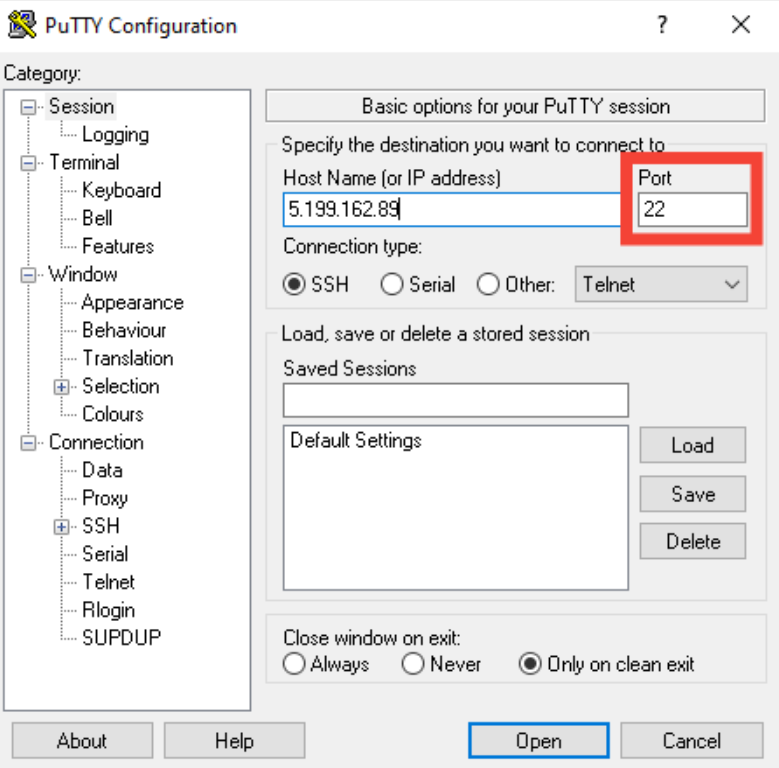
Specify a Custom SSH Port.
If your server uses a non-default port, append the -p flag to the command with the appropriate port number:
ssh username@ip_address -p custom_port
#Option B: Using PuTTY
PuTTY is a popular third-party SSH client for Windows users.
- Download and install PuTTY: Download PuTTY from the official website: https://www.putty.org and install it.
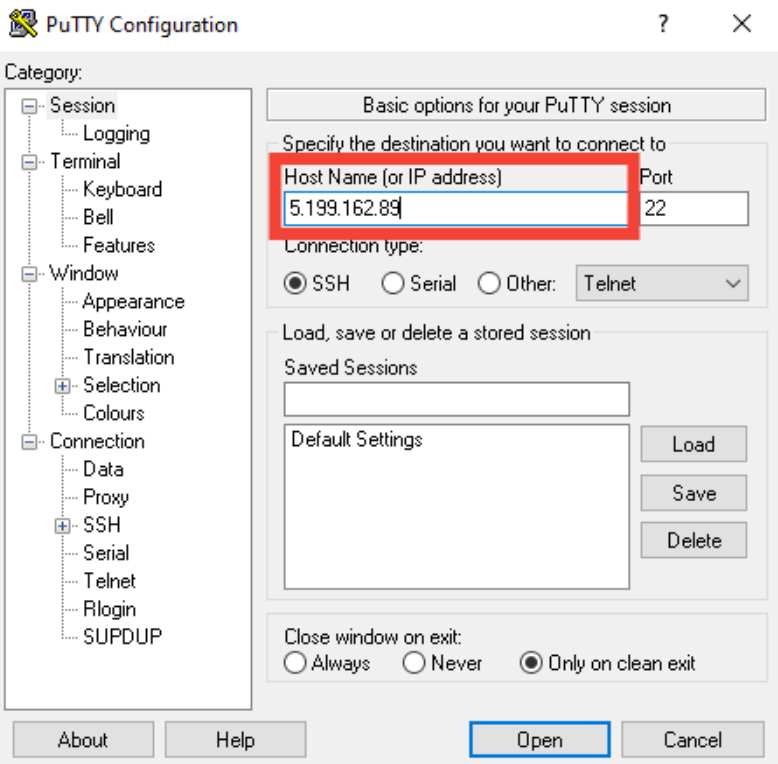
- Launch PuTTY: Open PuTTY from the Start menu or a desktop shortcut.
- Enter the server's IP address:
- Click the "Open" button to start the connection.
- Provide your username and password: When the terminal window appears, it will prompt you for your username and password. Enter the credentials to access the server.
#Closing the SSH Connection
Once you have finished working on the server, it’s essential to close the SSH session properly.
-
Type the Exit command.
To log out of the server and close the connection, type the following command and press "Enter":
exit -
Session Closed: The terminal window will close, or you’ll be returned to your local machine’s terminal.